Introduction
Unregulated borders and coastlines are the chinks in a nation’s homeland security armour. Smuggling (contraband and human trafficking), illegal immigration, and terrorism are the three threats, to a country’s security, most likely to exploit the porosity of unregulated borders and coastlines: think back to the “Mumbai: 26 November” attack, or think of the smuggling of contraband through Gujarat, Jammu & Kashmir, or Rajasthan.
Border/Coastal Surveillance Systems (B/CSS) address these chinks in the armour through a mix of sensors, command and control applications, and interception units. This brief details the components of a B/CSS solution and the desired features of a B/CSS solution, with reference to Homeland Security requirements.
The components of a B/CSS solution
The operational components of a B/CSS solution can be best represented through the flow-chart below:
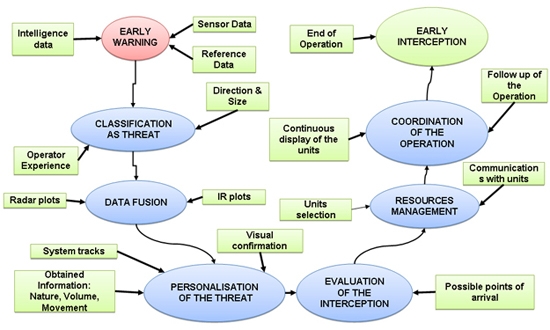
Sensor Network:
The sensor network serves as the eyes, ears, and skin of the B/CSS. A combination of sensors can track individuals and objects over varying distances, providing higher resolution as the target gets closer to the border or coastline. The functions of early-warning and threat-classification are carried out by the sensor network. Long-range sensors include OTH Radar, Sonar, SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar), and IR/Optical Cameras; while close-range sensors include fences, fence-mounted detectors, buried cable, volumetric sensors, and microwave sensors.
Command & Control Application:
A command and control application takes the inputs from the sensors and carries out data fusion of different types of sensors, maps the movement of highlighted objects on a cartographic representation of the border or coastline, generates SOPs for responding to potential threats, and collates data which will be used to generate reports for post-event analysis.
Operator:
The operator serves as the interface between the automated components of the B/CSS and the response teams on the field. Using the inputs provided by the command and control application, the operator directs the response teams to potential threats; sends real-time orders and missions to the response teams; and enters any additional information, received from the response units, into the command and control application.
Desiderata for a B/CSS solution
B/CSS solutions are characterized by a variety of architectures and feature-sets. However, there are a few features which are a must-have:
- Easy integration of sensors: The solution should allow the easy integration of new sensors, thus ensuring that the application does not have to be changed when a new sensor or sensor-group is introduced. Default support for a wide variety of sensors is another plus point.
- Publish/Subscribe mechanism: The sensor data should be managed by a Publish/Subscribe mechanism that allows sensors to publish data and authorized users to subscribe to it. This architecture ensures that there is low overhead in the system when handling 1000s of sensors and 100s of authorized users.
- Types of terrain: The solution should work in a variety of terrains – terrestrial, maritime, fluvial, and combined.
- Standards: The solution should support international standards used for identification and tracking commercial vehicles and vessels; such as AIS, VTS, and NFFI.
Conclusion
 Governments looking to exert greater control over activities at borders and coastlines, will do well to consider a B/CSS. The cost of setting up such a solution is trivial compared to the benefits arising out of implementing such a solution: reduced terror threats, and prevention of loss to the state exchequer through evasion of statutory levies and duties.
Governments looking to exert greater control over activities at borders and coastlines, will do well to consider a B/CSS. The cost of setting up such a solution is trivial compared to the benefits arising out of implementing such a solution: reduced terror threats, and prevention of loss to the state exchequer through evasion of statutory levies and duties.
Mistral offers the Amper 4ISR nemesis product line for Homeland Security needs in India. Amper’s nemesis BSS solution is targeted at governments requiring real-time monitoring and control of their borders and coastlines. Amper has implemented the nemesis BSS solution in Estonia, Serbia, and Spain; and has also been selected by the EU (European Union) to leads its initiative at defining an unregulated border architecture.
Amper’s nemesis BSS implementation in Spain has seen a significant reduction in illegal immigration and drug smuggling along Spain’s coast facing North Africa.



