Introduction
Biometrics is an automated method of recognizing or verifying a person based on a physical or behavioral characteristic. The features that are measured using biometrics include face fingerprints, palm, ear-lobe, handwriting, iris, retina, vein, and voice. Because each individual has a unique biometric print, security and verification solutions based on biometrics offer a better and more accurate means of ensuring application integrity, than passwords or access cards.
Biometrics Solutions
The key parameters that help identify if a human characteristic can be used for biometrics are listed below:
- Universality – the characteristic should be common to all individuals
- Uniqueness – how well the characteristic separates one individual from another
- Permanence – measures how well the characteristic resists aging and other variance over time
- Collectability – ease of capturing the characteristic for measurement
Some of the biometric techniques available in the market and /or gaining increasing popularity are listed below:
Physical Biometrics:
- Fingerprint – analyzing fingertip patterns
- Facial Recognition – measuring facial characteristics
- Hand Geometry – measuring the shape of the hand
- Iris Scan – analyzing features of colored ring of the eye
- Retinal Scan – analyzing blood vessels in the eye
- Vascular Patterns – analyzing vein patterns
- DNA – analyzing genetic makeup
Behavioral Biometrics Solutions:
- Speaker Recognition – analyzing vocal behavior
- Signature – analyzing signature dynamics
- Keystroke – measuring the time spacing of typed words
Other Biometric Solutions:
- Smart Cards – combining biometrics with identification cards
- Multi-biometrics – combining multiple types of biometrics for a single solution
By matching patterns of individuals against databases of records, users are better able to protect and secure their data and resources from crime and theft; that may earlier have been possible by false identities.
Biometric Systems
A biometric system can operate in two modes:
- Verification – This system does a one to one comparison of a captured biometric with a stored template to verify the individual identity. Can be done in conjunction with a smart card, username or ID number.
- Identification – This system does a one to many comparison of the captured biometric against a biometric database in attempt to identify an unknown individual. The identification only succeeds in identifying the individual if the comparison of the biometric sample to a template in the database falls within a defined threshold.
Any biometric device, consist of:
- A reader or scanning device
- Software that converts the scanned information into digital form and compares match points
- A database that stores the biometric data for comparison in an encrypted form; to prevent identity theft
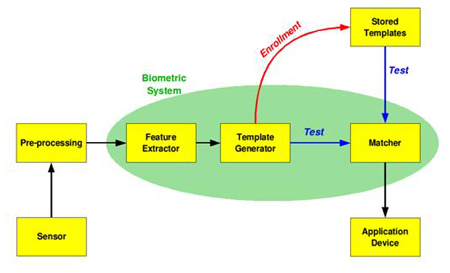 |
| Basic block diagram of a biometric system (Source: wikipedia.org) |
The first time an individual uses a biometric system is called an enrollment. During the enrollment, biometric information captured from the individual is stored into the database. In subsequent uses, biometric information is detected and compared with the information stored at the time of enrollment. It is crucial that storage and retrieval of such systems themselves be secure if the biometric system is to be robust.
Any biometrics based verification or identification process consists of three stages:
- The first stage (sensor/reader device) is an image acquisition system, which is the interface between the real world and the system; and has to acquire all the necessary data.
- The second stage involves the necessary pre-processing: removal clutter from the captured data, enhancement of the input and extraction of the necessary features. This stage is critical as the correct features need to be extracted in the optimal way. A vector of numbers or an image with particular properties is used to create a template. A template is a fusion of the relevant characteristics extracted from the source. Elements of the biometric measurement that are not used in the comparison algorithm are discarded in the template to reduce the file size and the data is encrypted to protect the identity of the enrollee.
- In the third stage, if an enrollment is being performed, the template is simply stored on a card or a database or both and/or if a matching is being performed, the obtained template is compared it with other existing templates, estimating the variance between them using an algorithm and a defined threshold. A successful match thus results into an output for a specified purpose (e.g. entrance in a restricted area).
Conclusion
Biometric technologies are fast becoming the foundation of an extensive array of highly secure identification and personal verification solutions. As the level of security breaches and transaction fraud increases, the need for highly secure identification and personal verification technologies is gaining increasing popularity.
Mistral Solutions, has partnered with L-1 ID, a leader biometrics solutions provider in the global market to leverage and provide the industry’s most advanced multi-modal biometric platforms for finger, face, palm and iris recognition, to the Indian market. Solutions for L-1 ID are used by most U.S. states and Canadian provinces and across 25+ countries. These solutions provide a circle of trust around all aspects of an identity and the credentials assigned to it. This includes proofing, enrollment, issuance and usage. For more information, visit http://www.mistralsolutions.com or email us at hs@mistralsolutions.com



